How Maths is Used in Space Exploration
1. Calculating Rocket Trajectories
Every space mission requires precise calculations to ensure a spacecraft reaches its destination. Scientists use Newton’s laws of motion and calculus to determine the correct velocity, acceleration, and thrust needed for a rocket to escape Earth’s gravity and enter orbit.
🔢 Example:
NASA’s Apollo 11 mission required advanced trigonometry and physics equations to ensure the spacecraft landed safely on the Moon and returned to Earth.
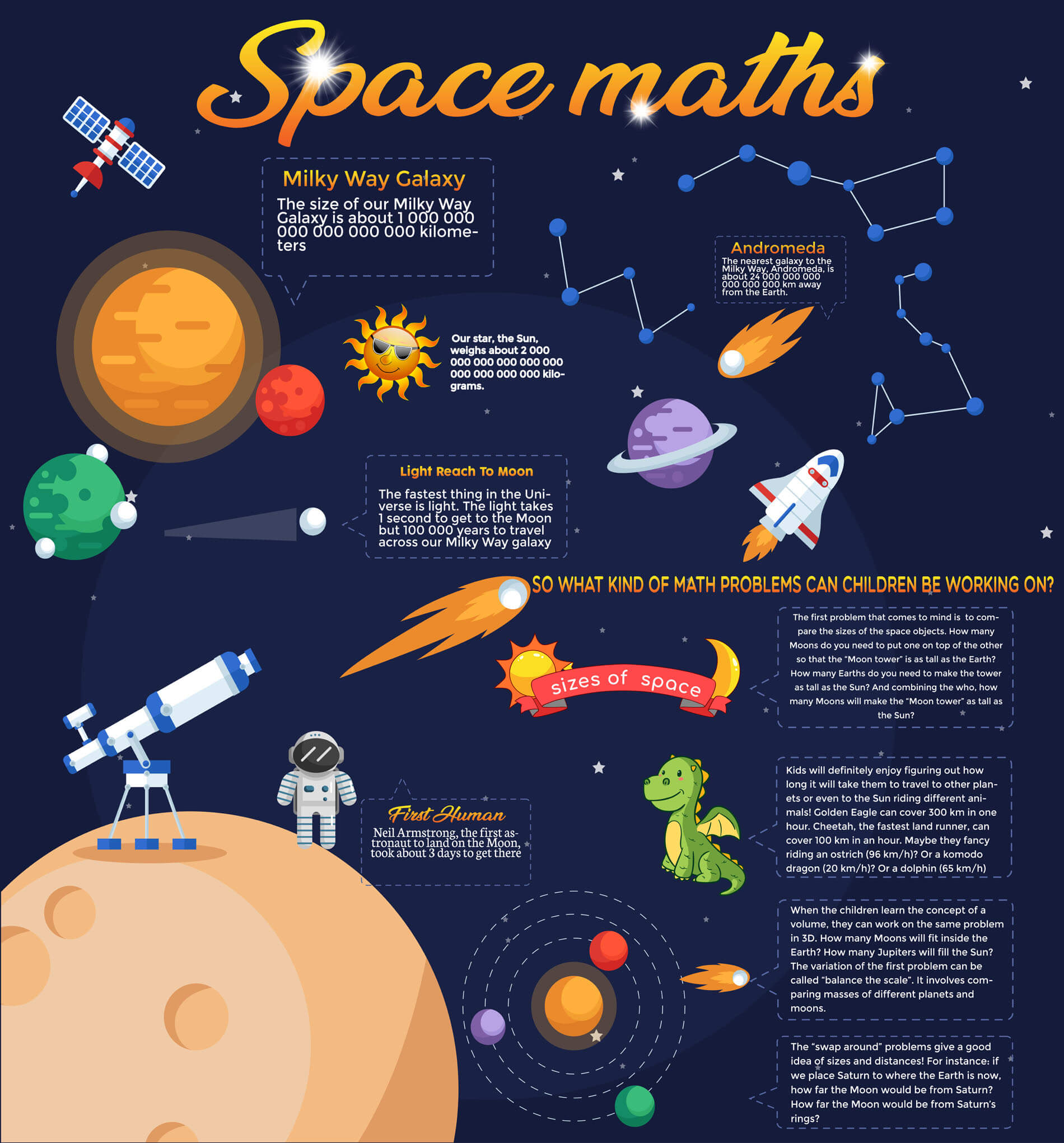
2. Measuring Distances in Space
Space is vast, and distances are measured in light-years, astronomical units (AU), and parsecs. Scientists use geometry and algebra to calculate distances between planets, stars, and galaxies using methods such as parallax and the inverse-square law.
🔢 Example:
Astronomers use the parallax method to determine the distance to nearby stars by measuring how their position appears to change relative to background stars as Earth orbits the Sun.
3. Predicting Planetary Orbits
Kepler’s laws of planetary motion help scientists understand how planets move around stars. These laws are based on complex mathematical equations that describe elliptical orbits, orbital speed, and gravitational forces.
🔢 Example:
Earth orbits the Sun in an elliptical path rather than a perfect circle. Mathematicians use Kepler’s Second Law to calculate how a planet’s speed changes depending on its distance from the Sun.
4. Time and Space Calculations
Astronomers rely on mathematical formulas to calculate time on other planets, predict solar and lunar eclipses, and measure the age of celestial objects.
🔢 Example:
A day on Mars (known as a “sol”) is 24 hours and 39 minutes. Scientists must adjust timekeeping when controlling Mars rovers like Curiosity and Perseverance.
Why Space Maths Matters
Understanding space through maths allows scientists to:
✅ Predict celestial events (e.g., eclipses, meteor showers).
✅ Navigate spacecraft accurately.
✅ Develop technology like GPS, which relies on space maths.
✅ Explore the possibility of interplanetary travel and colonisation.

